A 12-year-old NM DSH cat was presented for evaluation of inappetence for 3 days. Physical examination showed severe dental disease, gallop arrhythmia, and dull mentation. Abnormalities on serum biochemistry were hyperglycemia (270), elevated BUN (39) and ALT (473) activity, and severely elevated total protein (9.6) and globulins (6.8). Radiographs revealed hepatomegaly and a gas filled colon and small intestine.
A 12-year-old NM DSH cat was presented for evaluation of inappetence for 3 days. Physical examination showed severe dental disease, gallop arrhythmia, and dull mentation. Abnormalities on serum biochemistry were hyperglycemia (270), elevated BUN (39) and ALT (473) activity, and severely elevated total protein (9.6) and globulins (6.8). Radiographs revealed hepatomegaly and a gas filled colon and small intestine.
Liver – cholangio-hepatitis complex, neoplasia, granulomatous disease
Gall bladder – cholecystitis, obstruction (lith, neoplasia, duodenal/pancreatic disease
Pancreas – pancreatitis, neoplasia
Systemic – FIP, hyperthyroidism, multiple myeloma
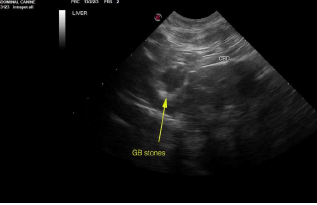
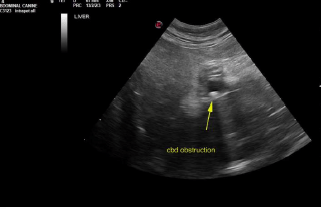
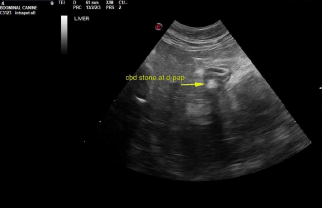
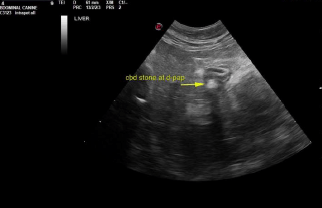
Common bile duct and duodenal papilla obstructive calculi. Gallbladder calculi.
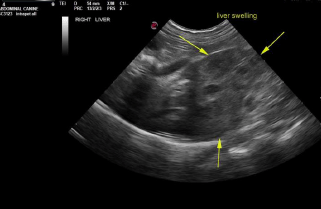
Liver in this patient presented heterogenous, irregular caudate process with capsular expansion. Recommend ultrasound guided FNA of this portion of the liver. Hepatoma possible, yet relatively rare in cats. Gallbladder presented thickened echogenic wall with calculi. Common bile duct was dilated with focal calculi. Near the duodenal papilla another was imbedded within the duodenal papilla. 0.5 cm calculus noted at the duodenal papilla causing posthepatic obstruction.
Surgical intervention with removal of the common bile duct and gallbladder calculi. Removal of the gallbladder likely ideal in this patient given the echogenic wall which usually indicates fibrosis. Sampling of the caudate process of the liver could also be considered first as a screening measure or direct sampling at surgery. This portion of the liver could also be removed directly; appears to be resectable.