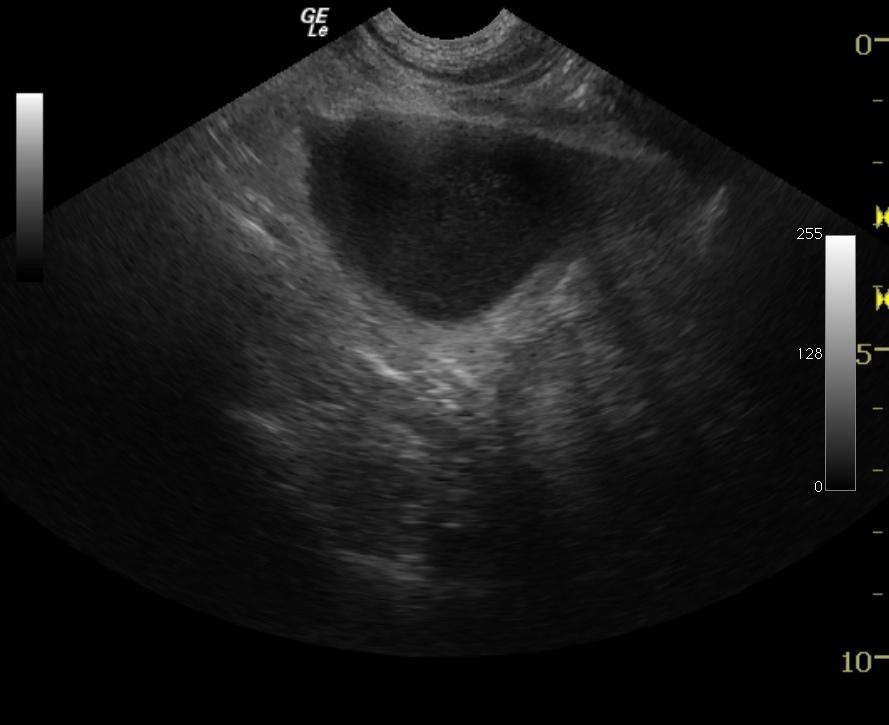
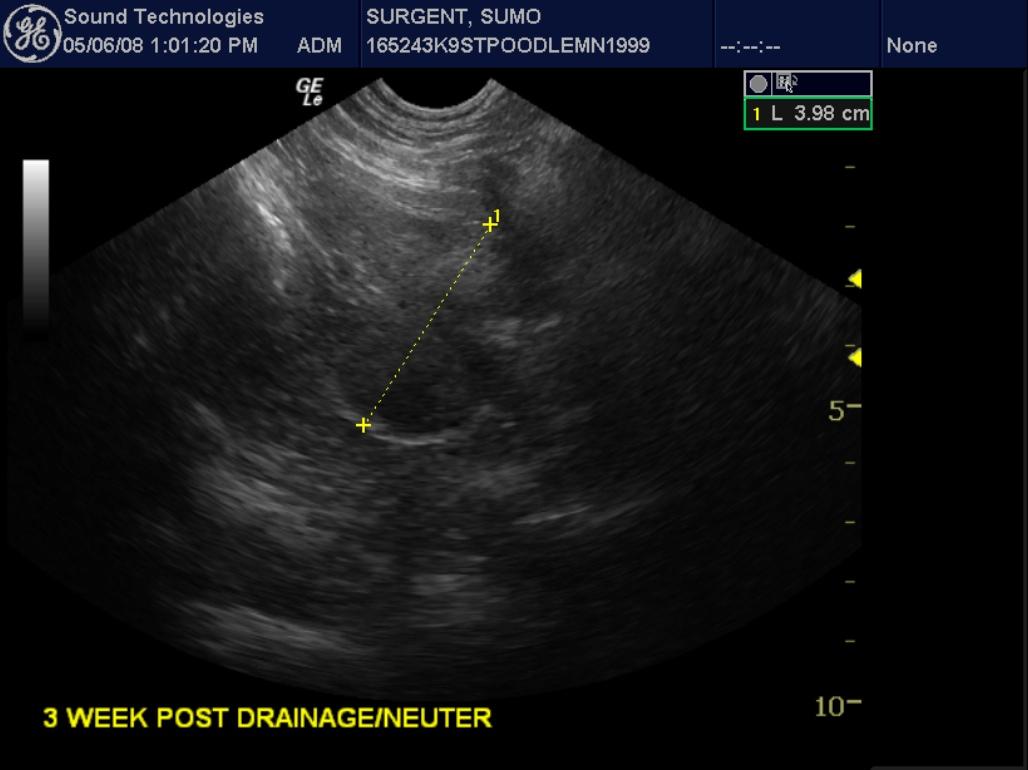
A 9-year-old MI poodle, with history of calcium oxalate crystalluria, presented for acting strangely. Per the owner, the patient was restless, had labored breathing, and was vomiting. There was a possibility of foreign body ingestion. On physical examination, the patient was depressed, quiet, and febrile, the mucous membranes were moist and pink, and the abdomen was non-painful on palpation. The only abnormality on blood chemistry was mild increase in ALT activity. The patient was treated with subcutaneous fluids, anti-emetics, and antibiotics.
A 9-year-old MI poodle, with history of calcium oxalate crystalluria, presented for acting strangely. Per the owner, the patient was restless, had labored breathing, and was vomiting. There was a possibility of foreign body ingestion. On physical examination, the patient was depressed, quiet, and febrile, the mucous membranes were moist and pink, and the abdomen was non-painful on palpation. The only abnormality on blood chemistry was mild increase in ALT activity. The patient was treated with subcutaneous fluids, anti-emetics, and antibiotics. At recheck examination he was still doing poorly, had difficulty moving around, and his appetite was decreased.